MODIFICATION OF HESTON’S MODEL FOR STOCK MARKET
Abstract
This research work is centred on the return on investment that informs investors and entrepreneurs on general performance of a company. The research problem was a modification of an existing model. This was done by incorporating rate of reinvestment of return and return on investment that follow random process. In addition to the modification, the existing model was extended from a two to four compartment stochastic differential equation. Formulation of a four- compartment stock market model was based on a four dimensional geometric Brownian motion. The compartments were that of stock price, stock price volatility, return on investment and return on investment volatility compartment. The solution of a four-compartment stock market model was proved to exist and also unique. The Octave programming language was used to implement the simplified stochastic Runge-Kutta
(SSR-K) scheme. Data were collected from Nigerian Stock Exchange (NSE) for the period of 2007 -2014 to validate the model formulated. It was found that, the stock price, stock price volatility, return on investment and return on investment volatility
follow random (stochastic) process. The correlation between the empirical stock price on the other hand and the corresponding computed values on the other hand from the model formulation was found to be significant as the significant value was zero
(0).The absolute error of the empirical return on investment and the corresponding computed values from the model formulation was found to be zero(0). Implying that, the computed results agreed very well with the empirical values. In addition, results
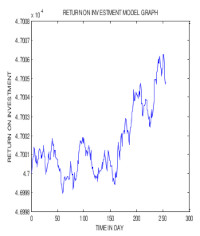
showed that stock price increases when return on investment decreases. We concluded that return on investment was considered to be the best index to use to study the general performance of companies rather than stock price.
Downloads
References
Cox, J.C., Ingersoll,J.E and Ross,S.A. (1985). A Theory of the Term Structure of Interest Rates, Econometrica. 53: 385–407.
Heston, S.L.(1993).A Closed-Form Solution for Options with Stochastic Volatility with Applications to Bond and Currency Options, Yale University. The Review of Financial Studies. 6(2):327-343.
Lin Chen (1996). Stochastic Mean and Stochastic Volatility — A Three-Factor Model of the Term Structure of Interest Rates and Its Application to the Pricing of Interest Rate Derivatives, Financial Markets, Institutions & Instruments. 5: 1–88.
Ologunde, A.O , D.O. Elumilade and T.O. Asaolu (2006). Stock Market Capitalization and Interest Rate in Nigeria: A Time Series Analysis. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics 4(1):234-245.
Gujarati, D.N. (2004).Basic Econometrics, 4th ed., Tata Graw – Hill Publishing Co. Ltd, New York. pp 1-4.
Abken, P.A.and Saikat,N. (1996).Options and Volatility,Economic Review. pp21-35.
Bekaert, G. (1995). Market Integration and Investment Barriers in Emerging Equity Markets.World Bank Economic Review.l( 9): 75-107.
Choudhury, T. (1996).Stock Markets Volatility and the crash of 1987: Evidence from Six Emerging Market. Journal of International Money and Finance.15: 969-981.
Bekaert, G. and Harvey, C. (1997). Emerging Equity Market Volatility. Journal of Financial Economics. 43: 29-78.
Ogbaji, Osayi and Ali Trans. Of NAMP Haque, M., and Hassan, M. K. (2000).Stability, Predictability and Volatility of Latin American Emerging Markets. University of Orleans. Orleans. pp7-18
Bekaert, G., and Wu, G. (2000).Asymmetric Volatility and Risk in Equity Markets. Review of Financial Studies.13:1-42.
French, K.R, Schwert, W. G., and Stambugh, R. F. (1987).Expected Stock Return and Volatility. Journal of Financial Economics.19:3- 29.
Baillie, R. and Degennaro, R. (1990).Stock Return and Volatility. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis. 25: 203-214.
Theodossiou, P. and Lee, U. (1995). Relationship between Volatility and Expected Return Across International Stock Markets. Journal of Business Finance and Accounting. 22(2): 289-300.
Nelson, D.B. (1991). Conditional Heteroskedasticity in Asset Returns. A New Approach, Econometrica. 59:347 – 370.
Glosten, L. R., Jagannathan, R., and Runkle, D. E. (1993).On the Relation Between the Expected Value and Volatility of the Nominal Excess Returns on Stocks.The Journal of Finance.48: 1779-1801.
Yuan,Y.(2013).Valuing a European Option with the Heston Model. M.Sc thesis in Applied and Computational Mathematics. Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, New York.p.13
Magnus,F.J.and Fosu,A. E. (2006).Modelling and Forecasting Volatility of Returns on the Ghana Stock Exchange Using Garch Models. American Journal of Applied Sciences. 3(10): 2042-2048.
Rashid A. and Ahmad S (2008).Predicting Stock Returns Volatility, An Evaluation of Linear vs Nonlinear Methods. International Research Journal of Finance Economic. 20: 141-150.
Abdelmoula, D.(2006).Stock price modelling:Theory and Practice.M.Sc thesis.Faculty of sciences, Vrije University, Amsterdam,Netherlands. pp 1-15
Jayasuriya, S. (2002).Does Stock Market Liberalization Affect the Volatility of Stock Returns, Evidence from Emerging Market Economies, Georgetown University Discussion Series.pp 3-18.
Ogum, G., Beer, F. and Nouyrigat,G.(2005).Emerging Equity Market Volatility. An Empirical Investigation of Markets in Kenya and Nigeria. Journal of African Business. 6(1/2): 139-154.
Olowe, R. A. (2009).Stock Return, Volatility and the Global Financial Crisis In An Emerging Market.The Nigerian Case. International Review of Business Research Papers.5(4): 426-447
Ahmed, E. A and Suliman,Z.S.(2011).Modelling Stock Market volatility using Garch models evidence from sudan. International journal of Business and social science.2(23):114:128.
Amir, R. and Kashif, U.R. (2011).Comparing the Prequencies of Different Frequencies of Stock Returns Volatility in Emerging Market: A Case Study of Pakistan. African Journal of Business Management. 5(1): 59-67.
Li, K. (2002).Long-memory versus Option-Implied Volatility Prediction. Journal of Derivatives. 9 (3): 9-25.
Rizwan M. F and Khan S (2007).Stock Return Volatility in Emerging Equity Market (Kse): The Relative Effects of Country and Global Factors. International Review of Business Research Papers.3(2): 362 - 375.
Aggarwal, R.,Inclan,C.and Leal, R. (1999).Volatility in Emerging Stock Markets, Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis. 34: 33-55.
Cohen K., Ness, W., Okuda, H., Schwartz, R., and Whitcomb, D. (1976).The Determinants of Common Stock Returns Volatility.An international Comparison, Journal of Finance.31:733-740.
Roll, R. (1992).Industrial Structure and the Comparative Behaviour of International Stock Market Indices. Journal of Finance. 47: 3-42.
Xing, X. (2004), Why Does Stock Market Volatility Differ across Countries? Evidence from Thirty Seven International Markets. International Journal of Business. 9(1): 83-102.
Harvey, C. R. (1995b),Predictable Risk and Return in Emerging Markets. The Review of Financial Studies. 8:773- 816
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Transactions of the Nigerian Association of Mathematical Physics

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.