INVESTIGATION OF GROUND WATER CAPACITY OF OKADA AND ITS ENVIRONS USING ELECTRICAL ESISTIVITY METHOD IN ACQUIFER POTENTIAL MAP
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60787/jnamp-v66-316Keywords:
Groundwater, resistivity, lithological, ferruginised clay stone, overburden, shaleAbstract
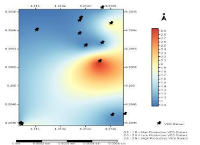
Electrical resistivity survey was carried out to investigate the groundwater capacity of Okada, an urban sedimentary area with the oldest Cretaceous rocks (sandstones and shales) which are of Albian age. The equipment used for the survey include, ABEM terrameter (SAS, 300C), four electrodes, hammer, four reels of wires, connecting cords, measuring tapes and global positioning system (GPS). This geological study was carried out in three different locations. The field layout employed was the Wenner-schlumberger array. The result of the survey shows that the average resistivities are 1337.8Ωm for the first layer, 5914. 34 Ωm for the second layer, 1277. 59 Ωm for the third layer, 189. 65 Ωm for the fourth layer and 695.78 Ωm for the fifth layer with probable lithologic interpretations as lateritic over-burden for the first layer,and highly compact clay stone for second layer, fissile dry shale, splintery shale(wet) and saturated and pyritised silty shale (wet) for the other three layers, respectively. The result indicates that potential groundwater is found in the fourth layer of the study area.
Downloads
References
. Debrill, H. (2008): Groundwater Hydrology. McGraw-Hill coy., New York.
. Allison, I.S, and Palmer, D.F,: Geology, the science of changing earth 7th edition. (2009), pg.445-467
. Ahuinox, B.E, Resistivity and Magnetic Survey for ground water in the Jos area of plateau. (2004): pg.78-95.
. Hellibramorfam, N.E.: Occurrence, Origin and Discharge of Groundwater, Dover, New York. (2013). Pg.556-578
. Freeze, R.A. and Cherry, J.A.: Groundwater, prentice-Hall Inc, Englewood Chiffs, new Jersey. (2018), Pg. 34-56.
. Gerald. D.H., and King R.F, (2011): Applied Geophysics, for Geologists and Engineers, pergamon press ltd. U.K.
. Esrilazar, B.C.E. and Okpoko, E.I.,: Gully erosion in the Accra region of Ghana. In: Challenges in African Hydrology: (2015) pg.335-347.
. Obini, N. Technical report of resistivity survey for groundwater at Ukpilla, submitted to Edo state government of Nigeria by Edo state Rural water Supply and Sanitation Agency (ED-RUWASA), Okada. (2005),pg.90-112.
. Juwvinaben, E.I, Groundwater pollution,Elsevier, Amsterdam international(2000)pg.4-8.
. Kearey, D and Brooks, M.O. : An introduction to geophysical exploration. Blackwell Scientific Publications (2012), pg.667-701.
. Lioyd, J.W. Case Studies in groundwater resources evaluation. Clerendum press oxford, (2017), pg43-52
. Todd, D.K. (2011) Groundwater hydrology. John Willery and sons Inc. Second Edition (2003), pg.45-72
. Ogriulex, M.E. The occurrence and exploitation of groundwater in Nigeria Basement rocks. Nigeria journal of Mining Geology (20`3) 67 ,pg.131-146.
. Telford, W.M. Geldart, L.P., Sheriff, D.A., Applied Geophysics Cambridge University press New York . (2014),pg.218-399.
. Jordan, E.E. Groundwater resource evaluation. McGraw-Hill publishing(2006) pg.1-9.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Journals of the Nigerian Association of Mathematical Physics

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.