INTEGRATED GEOPHYSICAL INVESTIGATION OF POLLUTION EXTENT IN A CEMETERY ENVIRONMENT: A CASE STUDY OF THE SECOND CEMETERY, BENIN CITY, SOUTH-SOUTH NIGERIA.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60787/jnamp.vol71no.605Keywords:
Leachate, Unconsolidated soils, Anomaly detection, VLF-EM profiling, Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT), Groundwater contaminationAbstract
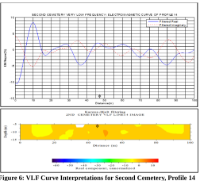
This study applied Very Low Frequency Electromagnetic (VLF-EM) profiling and Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) to investigate potential subsurface contamination within a cemetery environment in Benin City, Nigeria. Conductive anomalies detected from the VLF-EM survey were further examined using two-dimensional resistivity imaging. The ERT results revealed zones of markedly low resistivity (1–120 Ωm), characteristic of leachate-saturated, unconsolidated sandy soils. Several contaminant plumes were delineated, extending to depths of approximately 3–12 m, with some migrating downward toward the shallow aquifers that supply water to surrounding residential communities. These findings raise concerns regarding the potential degradation of groundwater quality in the area. The integrated VLF-EM/ERT approach proved effective in identifying conductive anomalies, enhancing interpretational confidence, and improving subsurface delineation within this complex burial setting.
Downloads
References
Rodrigues, L., 2002. Thesis presented for the degree of Master in Hydrobiology by the University of Porto, Oporto, Portugal.
Benson, A., Payne, K. and Stubben, M., 1997. Mapping groundwater contamination using dc resistivity and VLF geophysical methods -a case study, Geophysics, 62(1), 80-86.
Kalik, C. and Kaya, M.A. 2001. Investigation of Groundwater contamination using Electric and Electromagnetic methods at an open waste disposal site. A case study from Sparta, Turkey. Environmental Geology 40(6) springer-verlag.
Schraps, W.G., 1972. The relevance of soil filtration properties for the installation of cemeteries, 16, 225-229
Zychowski, J., Lach, J. and Kolber, M., 2000a. State and anthropogenic changes of water quality in Poland. Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Lodzkiego, Lodz. 1, 249-261.
Dumble, P. and Ruxton, C., 2000. Guidance on monitoring of landfill leachate, groundwater and surface water. Environment Agency, R&D Report. www.environment-agency.gov.ukhttp://publications.environment-agency.gov.uk/pdf/SCHO0404BGLA-e-e. pdf. Accessed 12 June 2013.
Creely, K.S., 2004. Infection risks and embalming. Research Report TM/04/01. www. iom-world.org/pubs/IOM_TM0401.pdf. Accessed 15 June 2013.
Environment Agency – UK, 2002. Assessing the groundwater pollution potential of cemetery developments. National Groundwater and Contaminated Land Centre. Bristol BS32 4UD, United Kingdom, pp. 1–20 http://www.cas.org/.
Dent, B.B., 2005. Vulnerability and the Unsaturated Zone – The Case for Cemeteries Proceedings “Where Waters Meet”. Joint Conference – New Zealand Hydrological Society, International Association of Hydrogeologists (Australian Chapter and New Zealand), Soil Science Society, Auckland, Nov 30 – Dec 2, 2005, paper A13 (pdf).
Knight, M.J. and Dent, B.B., 1998. Sustainability of waste and groundwater management systems. Proceedings of International Association of Hydrogeologists Sustainable Solutions Conference, Melbourne, February, pp. 359–374.
Bastianon, D., Matos, B.A., Aquino, W.F., Pacheco, A. and Mendes, J.M.B., 2000. Geophysical surveying to investigate groundwater contamination by a cemetery. The Annual Meeting of the Environmental and Engineering Geophysical Society. Arlington, pp. 709–718.
Braz, V.N., Silva, L.C.E. and Menezes, L.B.C., 2000. 1st joint World Congress on Groundwater, 2000, Fortaleza. Anais, Fortaleza, ABAS.
Chan, G.S., Scafe, M. and Emami, S., 1992. Cemeteries and groundwater: An examination of the potential contamination of groundwater by preservatives containing formaldehyde. Ontario Ministry of the Environment, Water Resources Branch Publication PIBS, 1813, pp. 1–11.
Zychowski, J., Lach, J. and Kolber, M., 2006a. The effect of bedding of mass graves from WW2 on chemical composition of groundwaters. In Ziutkiewicz, M. (ed.), State and anthropogenic changes of water quality in Poland. 5, 349-357.
Zychowski, J., Pawlikowski, M. and Lach, J., 2006b. Products from decomposition of organie compounds, example of a mass grave in Niepołomice near Cracow, Kwartalnik AGH, Kraków, Geologia, 32 (2): 203-224.
Zychowski, J., Lach, J. and Kolber, M., 2003. The occurrence of amino acids of glycine, leucine and isoleucine contents in the groundwater in cemeteries located on different bedrock. Geographia Polonica. 51 (11): 962-963.
Dent, B.B., 2000b. Decay products in cemetery ground waters. Geology and Sustainable Development: Challenges for the Third Millennium. 31st International Geological Congress, Rio de Janeiro. pp. 6–17.
Dent, B.B., 2002. The hydrogeological context of Cemetery operations and planning in Australia. Unpublished thesis submitted to the University of Technology, Sydney. 13-45
Trick, J.K., Williams, G.M., Noy, D.J., Moore, Y. and Reeder, S., 1999. Pollution potential of cemeteries: Impact of the 19th century Carter Gate Cemetery, Nottingham. British Geological Survey, Keyworth, Nottingham, United Kingdom (Technical Report WE/ 99/4, Environment Agency Technical Report NC/99/24), pp. 1–34.
Rodrigues, L. and Pacheco, A., 2003. Groundwater contamination from cemeteries cases of study. International Symposium Environment 2010 Situation and Perspectives for the European Union, Porto 6–10 May, Portugal.
Fisher, G.J. and Croukamp, L., 1993. Ground Water Contamination and its Consequences, Resulting from the Indiscriminate Placing of Cemeteries in the Third World Context. Conference Africa Needs Groundwater. University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa.
Alfoldi, L. and Croukamp, L., 1988. Problems and biological treatment, state of the art report. Watscitech 20 (3), 1–131.
Bitton, G., Farrah, S.R., Ruskin, R.H., Butner, J. and Chou, Y.J., 1983. Survival of pathogenic and indicator organisms in groundwater. Ground Water 21 (4), 405–410.
Zychowski, J., 2012. Impact of cemeteries on groundwater chemistry. Catena, ScienceDirect, 93, 29–37.
Morgan, O., 2004. Infectious disease risks from dead bodies following natural disasters. Revista Panamericana de Salud Pública, 15(5), 307–312.
Ucisik, A.S. and Rushbrook, P., 1998. The impact of cemeteries on the environment and public health – an introduction briefing. WHO Regional Office for Europe, World Health Organization. Report EUR/ICP/EHNA 01 04 01 (A), pp. 1–11.
Rotherham, J., 2011. The Bereavement Services Management Centre in the United Kingdom, The Crematorium Lodge, Brimington. Available online at: http://bsmconline.org.uk/research.htm
Van Haaren, F.W.J., 1951. Cemeteries as sources of groundwater contamination. Moorman’s Periodieke Pers, Den Haag, 35(16), 167–172.
Bouwer, H., 1978. Groundwater Hydrology. McGraw-Hill Inc., New York, NY, pp. 1–480.
Hanzlick, R., 1994. Embalming, body preparation, burial and disinterment: An overview for forensic pathologists. The American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology, 15, 122–131.
Gray, D.A., Mather, J.D. and Harrison, J.B., 1974. Review of groundwater pollution from waste disposal sites in England and Wales with provisional guidelines for future site selection. The Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology, 7, 181–196.
Eseigbe, J.O., Ufuah, M.E. and Ifatimehin, O.O., 2007. Sources of groundwater resource contamination in Benin Metropolis, Edo State. Confluence Journal of Environmental Studies, 2, 41–47.
Eseigbe, J.O. and Oisasoje, M.O., 2012. Aspects of gully erosion in Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria. Research on Humanities and Social Sciences, 2(7), 21–26.
Hansen, J.D. and Pringle, J.K., 2013. Comparison of magnetic, electrical and ground-penetrating radar surveys to detect buried forensic objects in semi-urban and domestic patio environments. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 13.
Reynolds, J.M., 1998. An Introduction to Applied and Environmental Geophysics. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., London, UK, 2nd Edition, 423 pp.
Telford, W.M., Geldart, L.P. and Sheriff, R.E., 2001. Applied Geophysics, 2nd Edition. Cambridge University Press, 343 pp.
Loke, M.H., 2014. Tutorial: 2D and 3D electrical imaging surveys. Available at: www.geotomosoft.com
Karous, M. and Hjelt, S.E., 1983. Linear filtering of VLF dip-angle measurements. Geophysical Prospecting, 31, 782–794.
Thomas, T., 2002. 2D resistivity and time-domain EM aquifer mapping: A case study north of Lake Naivasha, Kenya.
Ezenwa, I.M., Omoigberale, M., Abulu, R.R., Biose, E., Okpara, B.B. and Uyi, O., 2023. Burial leakage: A human-accustomed groundwater contaminant sources and health hazards study near cemeteries in Benin City, Nigeria. PLOS ONE, 18(12).
Ilaboya, I.R., Omosefe, E.B. and Ambrose-Agabi, E.E., 2024. Exploring the impact of cemetery leachates on groundwater quality in Benin City Metropolis, South-South Nigeria. Journal of Energy Technology and Environment, 6(2), 1–19.
Ambrose-Agabi, E.E., Izinyon, C.O. and Agbonaye, A.I., 2024. Evaluating groundwater contamination in the vicinity of a cemetery for environmental concerns. NIPES Journal of Science and Technology Research, 6(2), 270–280.
Idehen, O., 2020. A comparative investigation of groundwater contamination in typical dumpsites and cemeteries using ERT and physicochemical analysis of water in Benin Metropolis, Nigeria. Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 8, 72–85.
Afangideh, C.B. and Udokpoh, U.U., 2022. Environmental impact assessment of groundwater pollution within cemetery surroundings. Indian Journal of Engineering, 19(51), 100–115.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The Journals of the Nigerian Association of Mathematical Physics

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.