MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS OF A MONKEY-POX MODEL
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60787/tnamp.v23.624Keywords:
Transmission dynamics, Zoonotic disease, Local Global asymptotic stabilityAbstract
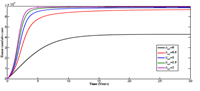
Monkey-pox is a relatively rare disease but with a case fatality rate of 1-10%. In this work, we formulated and analyze a mathematical model for the transmission dynamics of monkey-pox. We showed the existence of two equilibria namely, disease free and endemic equilibria. Both equilibria were shown to be globally stable. Sensitivity analysis showed that control strategies should be geared towards reducing contacts between susceptible humans and infected humans and infected non-humans. Also, numerical simulations showed that though human to human transmission may contribute to the incidence of monkey-pox in a population, the non-human to human transmission is seen to play more significant role in sustaining the transmission of monkey pox in a human population.
Downloads
References
Durski K.N., McCollum A.M., Nakazawa Y., Petersen B.W., Reynolds M.G., Briand S., Djingarey M.H., Olson V., Damon I.K. & Khalakdina A. (2018) Emergence of Monkey-pox West and Central Africa, 1970-2017.Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 67(10):306-310
Shchelkunov S.N., Marennikova S.S. & Moyer R.W. (2006) Orthopox viruses pathogenic for humans. New York: Springer Science & Business Media
Sklenovská N. & Van Ranst M. (2018) Emergence of monkey-pox as the most important orthopoxvirus infection in humans. Frontiers in Public Health 6:241.
Jezek Z., Szczeniowski M., Paluku K. & Mutombo M. (1987) Human Monkey-pox: clinical features of 282 patients. Journal of Infectious Diseases 156(2):293-298
Bankuru S.V., Kossol S., Hou W., Mahmoudi P., RychtáÅTM J., Taylor D. (2020) A game-theoretic model of Monkeypox to assess vaccination strategies. PeerJ 8:e9272 http://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.9272
Eteng W.E., Mandra A., Doty J., Yinka-Ogunleye A., Aruna S., Reynolds M.G., McCollum A.M., Davidson W., Wilkins K. & Saleh M.(2018) Notes from the Field: Responding to an Outbreak of Monkey-pox using the One Health Approach Nigeria, 2017-2018. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 67(37):1040-1041
Di Giulio D.B. & Eckburg P.B. (2004) Human monkey-pox: an emerging zoonosis. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 4(1):15-25
Usman, S. and Adamu, I.I. (2017) Modeling the Transmission Dynamics of the Monkey-pox Virus Infection with Treatment and Vaccination Interventions. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 5, 2335-2353.
Somma, S. A, Akinwande, N. I. and Chado, U. D A Mathematical Model of Monkey pox Virus Transmission Dynamics Ife Journal of Science vol.21, no. 1 (2019)
Bhunu, C.P. and Mushayabasa, S. (2011) Modeling the Transmission Dynamics of Pox-Like Infections. International Journal of Applied Mathematics,41, 2.
Chitnis N., Hyman, J.M., Cushing, J.M., (2008). Determining important parameters in the spread of malaria through the sensitivity analysis of a mathematical model. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 70, 1272-1296.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The Transactions of the Nigerian Association of Mathematical Physics

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.